Glands of the Endocrine System
The endocrine system is the collection of glands that produce hormones that regulate metabolism, growth and development, the internal balance of body systems, tissue function, sexual function, reproduction, response to stimuli (stress and/or injury), sleep, and mood.
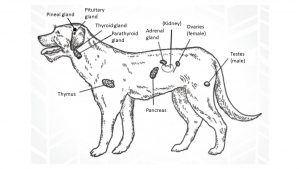
The endocrine system is made up of:
Pituitary gland
Thyroid gland
Parathyroid glands
Adrenal glands
Pancreas
Ovaries (females)
Testes (males)
Pineal gland (the last endocrine gland to have its function discovered)
Thymus (a double-duty gland that functions as both an endocrine and lymphatic gland, although it is only active until puberty).
The hypothalamus is the link between the endocrine and the nervous systems.
The word endocrine derives from the Greek words “endo” meaning within, and “crinis”, meaning to secrete.
In general, a gland selects and removes materials from the blood, processes them and then secretes the finished chemical product (hormone) back into the blood for use somewhere in the body. Each type of hormone produced is targeted towards certain organs and tissues.
The endocrine system does get some help from other organs such as the kidney, liver, heart and gonads, which all have secondary endocrine functions.
